- Sep 25 2024 The appointment system for the doctors of Molly Al-Movahedin Clinic opens every Friday at 2:00 p.m
- Sep 15 2024 The ceremony of honoring and introducing directors of medical sciences and honoring exemplary staff was held
- Sep 10 2024 The visit of the head of medical sciences to the installation site of advanced extracorporeal stone breaking device
- Aug 20 2024 Molly Al-Movahedin Ali Gerash clinic was equipped with a biometric device (eye lens determination)
- Aug 11 2024 Three appointments (transfers) in Gerash Medical Sciences
- Jul 25 2024 A scientific conference was held in the medical sciences
- Jun 30 2024 Removing the 11 kg tumor from the patients abdomen in Gerash Hospital
- May 21 2024 The condolence message of head of Gerash Medical Sciences following the martyrdom of the popular and revolutionary president Ayatollah Raisi and his companions
- May 6 2024 International work and worker Day ceremony at the conference hall of the University of Medical Sciences
- Apr 1 2024 Operation of advanced brain and neurosurgery microscope for the first time in Gerash Hospital's operating room
General and Onco Surgery:
Surgical oncology may be used to: Diagnose cancer (diagnostic surgery or biopsy) Remove a tumor or a portion of the cancer (curative or debulking surgery) Determine where the cancer is located, whether it has spread and if it is affecting the functions of other organs (staging surgery)

Cosmetic Surgery:
Cosmetic surgery, also known as aesthetic surgery, is where a person chooses to have an operation, or invasive medical procedure, to change their physical appearance for aesthetic reasons. Aesthetic surgery can provide profound health benefits to patients - both physically and for their psychosocial wellbeing.

Urology onco surgery:
Urology is the management of patients presenting with conditions affecting the urinary tract, and of the male reproductive organs. Typically, there are more male urology patients than female patients, and the service has a high proportion of older patients.
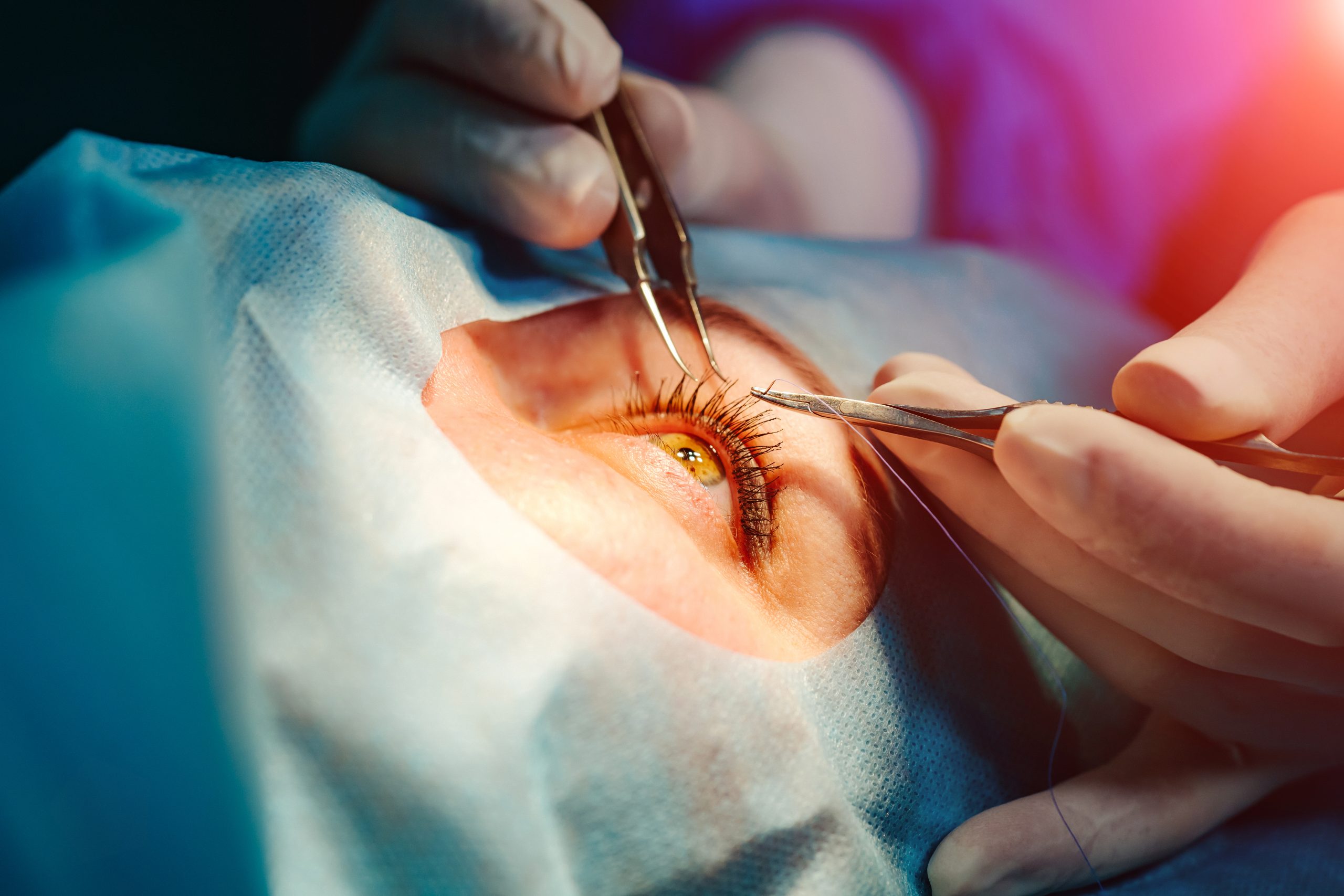
Ophthalmic surgery:
Surgical ophthalmology refers to ophthalmologists who perform microsurgical intraocular operations, such as cataract extraction surgery or retinal detachment repair surgery. Interventional cardiac surgery:
Radio therapy:
Radiation therapy uses x-rays to destroy or injure cancer cells so they cannot multiply. Radiation therapy can be used to treat the primary cancer or advanced cancer. It can also be used to reduce the size of the cancer and relieve pain, discomfort or other symptoms.

انتخاب حالت کور رنگی
سرخ کوری سبز کوری آبی کوری سرخ دشوار بینی سبز دشوار بینی آبی دشوار بینی تک رنگ بینی تک رنگ بینی مخروطیتغییر اندازه فونت:
تغییر فاصله بین کلمات:
تغییر فاصله بین خطوط:
تغییر نوع موس:

